
16-03-2023 | Healthy meals
Phosphorus is an element that can be found in all living organisms, mostly as organically bound phosphates, which makes it an essential macroelement. Phosphorus is in the structure of DNA and RNA, it is also a constituent of compounds with high energy adenosine triphsphate (ATP) and creatine phosphate (CP) and phospholipids which are the structural components of all cellular membranes. 85 – 90 % of total phosphorus is found in bone and teeth in the form of hydroxyapatite.

Although phosphorus is indispensable for the normal functioning of cells, the intake of a large amount of phosphorus in the body can cause certain health problems. The disruption of the calcium and phosphorus ratios in the body can lead to certain hormonal disorders, the excess of phosphorus disrupts the absorption of calcium in the intestine, where as a consequence is the release of calcium from the bones and their softening.
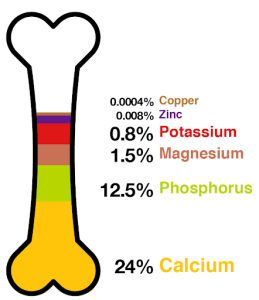

As we know, the food is the main source of phosphorus for all living organisms. For humans, the largest source of phosphorus is meat and meat products, where the origin of phosphorus may be natural and added (as a food additive). In processed meat, phosphates are added as a agents for binding water, to obtain a better texture of the product, for the emulsification of fats, to retain the color of the meat, to prevent oxidation of fatty acids and to stabilize the pH value. Due to the increasing use of phosphates in the production of meat and meat products, the intake of phosphorus in the body increases, and hence the risk of some metabolic disorder.

In order to prevent the excessive use of phosphates in the diet, each country has a National Regulation that prescribes the maximum content of phosphorus in food. In our country, Rulebook on additives that can be used for food production prescribes added phosphorus content phosphorus (as P2O5) can be added in meat products up to 5.00 g in 1 kg meat. Unlike the National Regulation in some countries, which allows a total phosphorus content (as P2O5) of up to 8 g in 1 kg of meat, our National Regulation has not yet prescribed the permissible total phosphorus content in meat and meat products.
MSc Emilija Gjorgieva,
Master of Chemical Sciences

16-03-2023 | Healthy meals
Proteins together with carbohydrates and fats present a part that is never left out in a balanced diet. They are one of three basic groups of macronutrients that are necessary for the organism to function normally, i.e. they are necessary for different metabolic processes. They can be found everywhere in the human body- in the muscles, bones, skin, hair, and literally in every cell in the organism. There are 10000 different types of proteins that make you what you are – a whole human organism. Proteins are made from amino acids. The organism can create some of these amino acids by itself and they are called nonessential amino acids, while it must take others through food and this group of amino acids is called essential amino acids.
How many grams of protein should I intake?
Depending on the basic metabolic needs, the minimal amount of protein intake is somewhere around 0.8g protein per kilogram of body weight per day. I.e., if a person weighs 70 kilograms then 50 grams of protein are needed daily. However, the need for protein intake varies depending on the physical activity and the fitness goals that you have. If you want to build muscle mass then you would need to have a higher protein intake. Another piece of important data is what percentage of the total caloric intake should come from proteins. The recommended percentage is 10-35%. What does that mean? For a person who has a daily intake of 2000 calories, 200-700 of them should be from proteins, which equals to 50-175 grams per protein per day.
How much protein does food contain?
We often ask ourselves which foods contain a high level of proteins or rather how should we take them. This depends on personal preference and way of nutrition. The biggest amount of protein is found in foods of animal origin like meat, fish, eggs, milk and dairy. On the other hand, plant-based proteins can be found in beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu cheese, nuts and soy. The people who practice vegetarianism or have a vegan diet get their protein from plant products. Different types of foods contain a different amount of protein per 100 grams. As an example, we will show you some of the most commonly used foods.
Examples of foods with the amount of protein they contain
| Protein from animal products |
Amount of proteins(g) per 100g |
|
| Meat |
Chicken
Pork
Beef |
32.0
31.6
31.0 |
| Fish |
Canned tuna
Salmon |
24.9
24.6 |
| Eggs |
Chicken eggs (boiled) |
14.1 |
| Dairy products |
Milk
Cottage cheese
Greek yogurt |
3.4
9.4
5.7 |
| Plant-based protein |
Amount of protein (g) per 100g |
|
| Lentil |
Red lentils (boiled)
Chickpeas (in a can) |
7.6
7.2 |
| Legumes |
Tofu
Beans (in a can) |
8.1
6.9 |
| Cereals |
Rice
Bread (Whole-grain)
Bread (white)
Pasta |
10.9
7.9
7.9
4.8 |
| Nuts |
Almonds
Walnuts
Hazelnuts |
21.1
14.7
14.1 |
Ile Kuzmnoski, MD

16-03-2023 | Healthy meals
What are fats?
Fat is one of the three macronutrients that are essential for human health, along with carbohydrates and protein. Fats play a number of important roles in the body, including providing energy, helping to absorb and transport vitamins and minerals, and supporting cell growth and development.
Types of fats?
There are different types of fats, including saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated and trans fats. Saturated fats are typically found in animal products such as meat and dairy, and are solid at room temperature.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, on the other hand, are typically found in plant-based foods such as nuts, seeds, and oils, and are liquid at room temperature.
Trans fats, also known as partially hydrogenated oils, are typically found in processed foods and are created through a process of adding hydrogen atoms to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid.
Saturated fats have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, and it is recommended that people limit their intake of these fats.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, on the other hand, have been shown to have a number of health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and improving cholesterol levels. One type of polyunsaturated fat, omega-3 fatty acids, is particularly important for human health. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in foods such as fish, nuts, and seeds, and are important for brain and heart health. Trans fats, however, have been shown to have negative effects on health. They are known to increase the risk of heart disease by raising “bad” LDL cholesterol levels and lowering “good” HDL cholesterol levels. They also increase inflammation in the body, which can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. It is recommended to avoid trans fats as much as possible, and to check food labels for partially hydrogenated oils. The American Heart Association recommends that adults limit their intake of saturated and trans fats, and aim to get most of their fat intake from monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
What kind of fats should I consume?
Fats are an important macronutrient that play a number of important roles in the body. However, it is important to be mindful of the different types of fats and to consume them in moderation. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, are particularly beneficial for human health. Trans fats, on the other hand, should be avoided as much as possible, as they have been shown to have negative effects on health.
How much fats should I consume?
The association recommends that adults should aim to get no more than 5-6% of their daily calories from saturated fats, and that trans fats should be avoided as much as possible. The American Dietetic Association recommends that adults should consume 20-35% of their daily calories from fats. This would mean for a person consuming 2000 calories a day, 400 to 700 calories should come from fats. This is a general recommendation and it can vary based on the specific needs and goals of the individual. It is important to note that the specific recommendations for fat intake can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of fat intake for your individual needs.
Ile Kuzmanoski. MD

16-03-2023 | Tips for better sleep
Sleep is an essential part of overall health and well-being, and quality of sleep is especially important for young adults. Adequate sleep is essential for physical and mental health, and it helps to improve memory, learning, and cognitive function. However, many young adults struggle with sleep, and poor sleep can lead to a range of problems, including fatigue, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. One of the most important factors that affect sleep quality is sleep habits. Many young adults struggle with maintaining regular sleep schedules, and this can lead to problems with insomnia and other sleep disorders.
How to improve sleep quality?
To improve sleep quality, it is essential to establish regular sleep patterns, including going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Another important factor that affects sleep quality is the environment. The bedroom should be dark, cool, and quiet, and it should be free from distractions such as electronic devices. Using earplugs or a white noise machine can help to block out noise and make it easier to fall asleep. There are also a number of techniques that can be used to improve sleep quality, including relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and meditation. Exercise is also an effective way to improve sleep, as it helps to reduce stress and improve overall health. However, it is important to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it can make it harder to fall asleep.
How long should I sleep?
The recommended amount of sleep for young adults is 7-9 hours per night. However, the specific sleep needs can vary depending on the individual. Factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health can all affect the amount of sleep needed to feel rested and refreshed.
What is the role of time management?
Time management is another important factor that can affect sleep quality. Many young adults struggle to balance school, work, and social obligations, and this can lead to stress and fatigue. To organize your time better, it is important to prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and avoid procrastination. It is also important to schedule in time for relaxation and leisure activities, as these can help to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, sleep is an essential part of overall health and well-being, and quality of sleep is especially important for young adults. To improve sleep quality, it is essential to establish regular sleep patterns, create a conducive environment, use relaxation techniques and exercise, and manage time effectively. It is also important to prioritize self care and leisure activities, as these can help to reduce stress and improve overall well-being. However, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any sleep problems or concerns.
Ile Kuzmanoski, MD

16-03-2023 | Tips for better sleep
The quality of sleep is closely linked to overall health and well-being, and two key factors that can affect sleep quality are nutrition and exercise. A healthy diet and regular physical activity can both have a positive impact on sleep, and incorporating certain foods and exercises into your daily routine can help to improve the quality of sleep.
A healthy diet is essential for good sleep. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help to improve sleep quality. It is also important to limit processed foods and foods high in sugar, as these can have a negative impact on sleep.Some specific foods that have been shown to improve sleep include:
- Cherries: These are a natural source of melatonin, a hormone that helps to regulate sleep.
- Milk and dairy products: These are high in calcium, which has been shown to help improve sleep.
- Fish: Fish such as salmon and tuna are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to improved sleep.
- Nuts and seeds: These are rich in magnesium, which has been shown to help improve sleep.
Regular exercise is also essential for good sleep. Exercise helps to reduce stress and improve overall health, which can have a positive impact on sleep. However, it is important to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it can make it harder to fall asleep. Some specific exercises that have been shown to improve sleep include:
- Yoga: Yoga can help to reduce stress and improve relaxation, which can help to improve sleep.
- Aerobic exercises: Aerobic exercises such as cycling, swimming, and running can help to improve sleep quality.
- Weight training: Weight training can help to improve the overall quality of sleep.
In conclusion, nutrition and exercise are both important factors that can affect the quality of sleep. A healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, as well as specific foods that improve sleep, is essential. Regular exercise, especially yoga, aerobic exercises, and weight training can also help to improve sleep quality, but it is important to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new diet or exercise routine if you have any concerns.
Ile Kuzmanoski, MD
















